In this tutorial, we will simulate a runaway reaction scenario, which is a situation where chemical process becomes uncontrollable, leading to a rapid increase in temperature. Understanding the conditions that lead to such a reaction is crucial for preventing dangerous accidents in industrial processes. We will use non-isothermal batch reactor in Softinery web app:

Setting the parameters
First, let’s set the parameters of the process. We will define parameters corresponding to a gas phase in slightly increased pressure. Chosen parameters are the following:
- Density: 22 kg/m3 (step 1 on the image below)
- Specific heat: 1000 J/(kg·K) (step 2)
- Reaction enthalpy: -500 kJ/mol (step 3)
- Initial substrate concentration: 40 mol/m3 (step 5)
- Pre-exponential factor: 0.1·104 1/s (step 4)
The remaining process parameters can be left at their default values. You can decrease process time a little to focus on the initial period. We did not change the default reaction so it is set to A1 → B1 (see green rectangle in the figure below).

Reaction and Temperature Dynamics
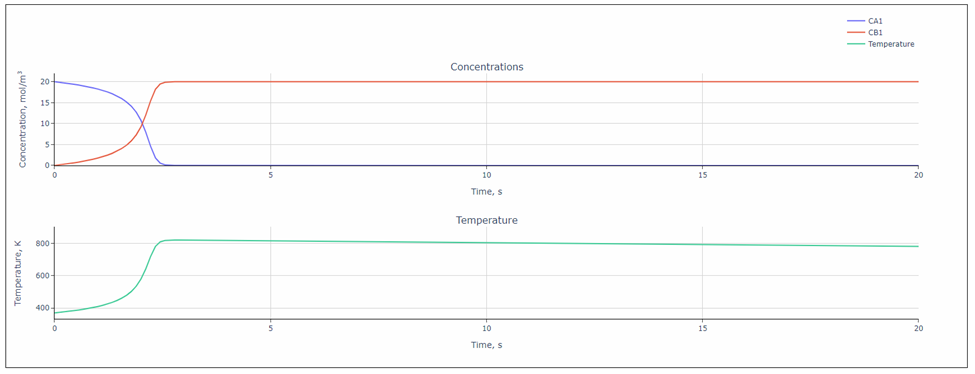
The enthalpy of the reaction indicates that a significant amount of heat is released during the process (negative value represents exothermal reaction). Given the low specific heat capacity of the gas, this could cause a rapid temperature rise if the generated heat is not dissipated quickly.
After setting the parameters, the process simulation is performed automatically. The result shows the concentration and temperature profiles over time (figure below). We can see that the reaction proceeds very rapidly. In just 1.2 seconds, the temperature rose to over 1278°C. Such a rapid reaction process would be very dangerous in a real-world scenario.

Importance of Safe Process Design
Understanding the dynamics is crucial for designing safe and efficient processes. Simulating reactions like this can help identify potential hazards before implementing them in real-world industrial settings. If the temperature rise is too rapid, as in the case of this simulation, it indicates that additional cooling or process adjustments are needed.
How to avoid runaway reaction?
Please try to increase values for heat removal, that is heat transfer coefficient and heat transfer area. For sufficiently high values the excessive temperature should be avoided. Another solution is to decrease initial substrate concentration, which in reality can be obtained by decreasing pressure. The figure below shows the results for an initial substrate concentration that is halved and a heat transfer area that is doubled. We observe that the temperature is much lower than before, but it is still very high (over 820°C).
Custom Software Solutions to Optimize Your Chemical Processes
Our software solutions are tailored to meet the specific needs of the chemical industry. Whether you’re optimizing reactors, heat exchangers, or other critical processes, we develop custom tools that deliver precision, efficiency, and innovation. With our solutions, you can enhance process control, reduce costs, and improve overall performance. Let’s discuss how we can create software that fits your unique requirements and drives your operations forward.
Contact me to find out how our tools can help your company ensure safety and maximize process efficiency.
Related posts
Chemical equilibrium – Scilab
Tubular reactor
Stay Connected
If you want to learn more about simulation and mathematical modelling in process engineering, please follow us on LinkedIn:
https://www.linkedin.com/company/90977334
Facebook:
https://facebook.com/softinery
Blog: